| Kelley and Conner's Emotional Cycle of Change Keeping Going When You Make a Voluntary Change | ||||
|
||||
|
About the Tool Don Kelley and Daryl Conner developed their Emotional Cycle of Change model in the mid-1970s, and they outlined it in the "1979 Annual Handbook for Group Facilitators." The cycle has five stages, shown in figure 1, below. Stage 1: Uninformed optimism. Stage 2: Informed pessimism. Stage 3: Hopeful realism. Stage 4: Informed optimism. Stage 5: Completion. Figure 1 - The Emotional Cycle of Change 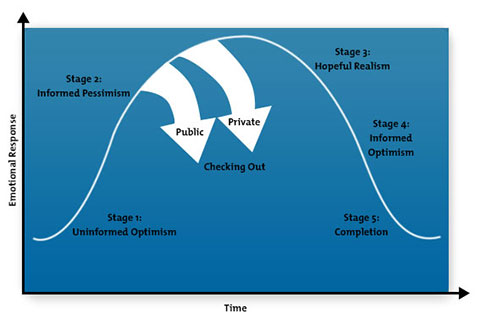 List and image from "Change Thinking," by Daryl Conner. © 2012 Conner Partners. Used with permission. The figure above outlines how your emotional response - the extent to which you react emotionally to something, based on how much it will affect you personally - is likely to alter as you go through a change. It rises as you move through a stage of pessimism, and falls as you become more confident with your project.
How to Apply the Model You can use the five stages outlined in this model to anticipate your emotional responses after you make a change, so that you can deal with them better. Below, we look at each stage in detail, and we outline tools that you can use to cope with your changing emotional responses. Stage 1: Uninformed Optimism In stage 1, you may be excited to get started, but your emotional response levels will be low, as you'll be focused on doing, rather than thinking. However, you may not be aware of the difficulties that you could face along the way. Capitalize on your excitement: make a treasure map, and draw up a list of the benefits that you hope to achieve. These will motivate you later on, when times get tougher. Stage 2: Informed Pessimism As your new situation progresses, you may start to feel some negative emotions about the project, especially if you hit problems. For example, you may become frustrated by challenges, or anxious about your ability to meet your goal. You may even want to quit altogether. This is the point at which many projects fail. It's also the point at which many people "check out" of a project. Kelley and Conner noted that this can happen in two ways.
You may also want to look for a mentor or support network to help you deal with challenges and self-sabotaging thoughts. Alternatively, try to keep a journal. The more you verbalize your doubts and fears, the easier they are to address. Stage 3: Hopeful Realism Once you've pushed past doubt, your pessimism should start to decline. You may still feel anxious, but you're more likely to be able to solve problems, because you're now more familiar with your situation. Use action plans or project management tools to keep on top of tasks, and look for ways to build habits that support the change that you've made. For example, if you've signed up to a new class, set aside regular times for study, and ask friends or colleagues to check in with you to see how you're doing. Stage 4: Informed Optimism In this phase, you'll start to feel confident that you've made the right choice. You'll look at the change with more experienced eyes, and you'll feel less anxious about problems. Use affirmations to make sure that you stay positive. You may now be in a position to support others who are at an earlier stage of the change process. For example, you could offer to be a "study buddy" or mentor to someone starting out in a new class, or offer to share your new knowledge with colleagues. This is an effective way to cement new information, and you may even inspire someone to embark on a similar change. Stage 5: Completion You'll probably feel very satisfied when you reach your goal. Your emotional response levels will have lowered, now that you've worked through the problems and brought about the change. Celebrate your success, and thank people who supported you during the change process. Finally, before you move on, reflect on what went well, and what you learned. This kind of project review will boost your self-confidence, and it can help you with similar projects in the future. Key Points Don Kelley and Daryl Conner developed the Emotional Cycle of Change, and explained it in the "1979 Annual Handbook for Group Facilitators." The model outlines the five emotional stages that most people go through during voluntary change: Stage 1: Uninformed optimism. Stage 2: Informed pessimism. Stage 3: Hopeful realism. Stage 4: Informed optimism. Stage 5: Completion. When you understand these five stages, you can prepare yourself for the practical and the emotional impacts of the changes that you decide to make. |
Thursday, November 7, 2013
Planning Personal Change? Know This!
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)





No comments:
Post a Comment